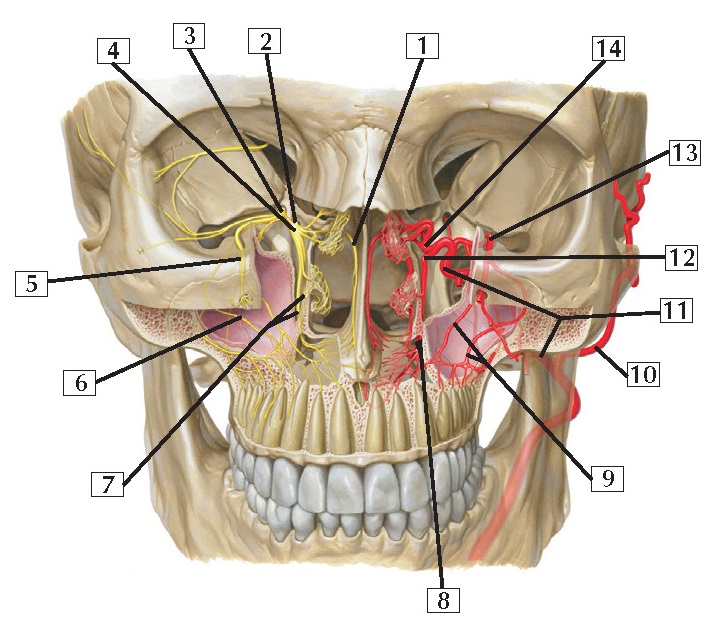
Pterygopalatine Fossa Anatomy
1. Nasopalatine nerve (septal branch)
2. Pterygoid canal (behind ganglionic
branches connecting maxillary nerve [CN V2] and
pterygopalatine ganglion)
3. Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
4. Pterygopalatine ganglion
5. Infra-orbital nerve
6. Posterior superior alveolar nerve
7. Greater and lesser palatine nerves
8. Lesser and greater palatine arteries
9. Anterior and middle superior
alveolar arteries
10. Superficial temporal artery
11. Maxillary artery
12. Descending palatine artery
13. Infra-orbital artery
14. Sphenopalatine artery
Comment: Nerves are shown on 1 side and arteries on the
other. This region is largely supplied by branches of the maxillary nerve (V2)
and by arterial branches of the maxillary artery from the external carotid. The
maxillary teeth and gums are supplied by the posterior, middle, and anterior superior alveolar
neurovascular bundles.
Clinical: Midface fractures (Le Fort fractures) and/or
blowout fractures of the orbital floor may damage the branches of the maxillary
nerve, affecting not only sensory modalities related to the distribution of the
nerve but also the parasympathetic postganglionic
secretomotor fibers that join the branches of this nerve after they leave the
pterygopalatine ganglion (site of the postganglionic
parasympathetic neurons).