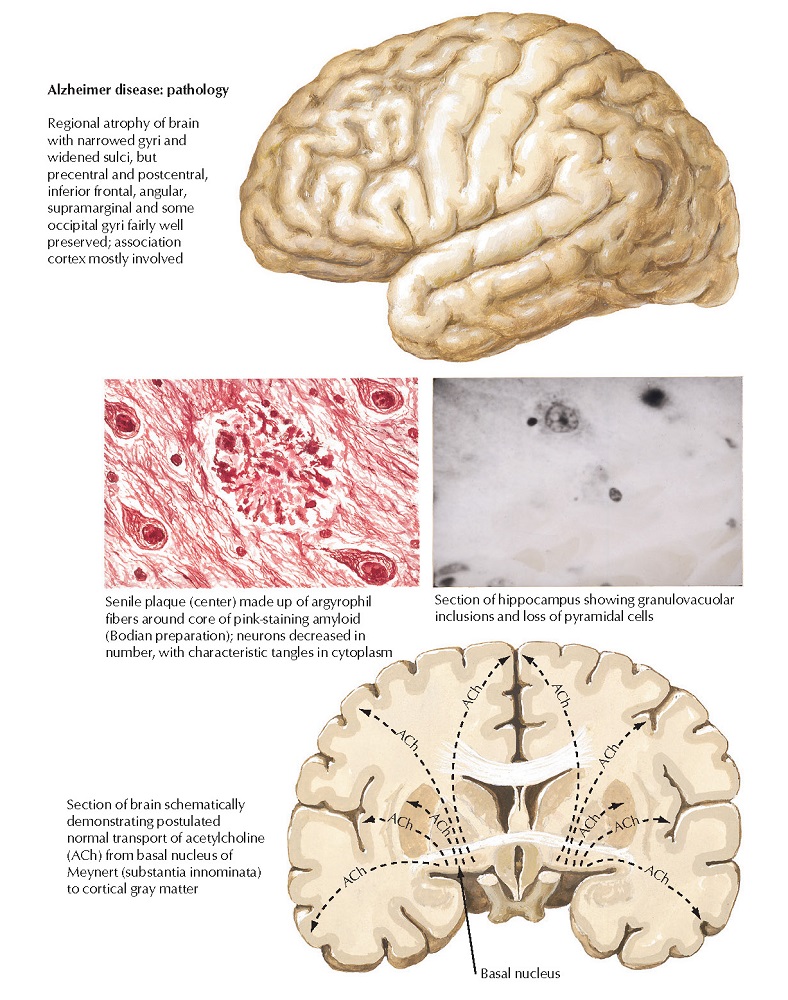
Alzheimer Disease: Cholinergic Involvement and Drugs
Although many neurotransmitter systems become disrupted in Alzheimer disease, cholinergic pathways become
especially damaged. Functional cholinergic deficits, such as impairment in
shortterm memory, become apparent even in the early stages of the disease. Medication strategies to ameliorate
the decline in cholinergic
function include the administration of precursors (eg, lecithin); directacting
cholinergic receptor agonists; and indirectacting cholinomimetics.
Indirectacting agents, specifically cholinesterase
inhibitors, such as donepezil, galantamine, and rivastigmine,
are currently the most commonly used. Ongoing research is investigating other
potential targets, such as enzymes responsible
for synthesis or degradation of Aβ or τ protein, and other postulated mechanisms
responsible for the etiology or progression of the disease.