Bronchi Anatomy
The bifurcation of the trachea in the mediastinum
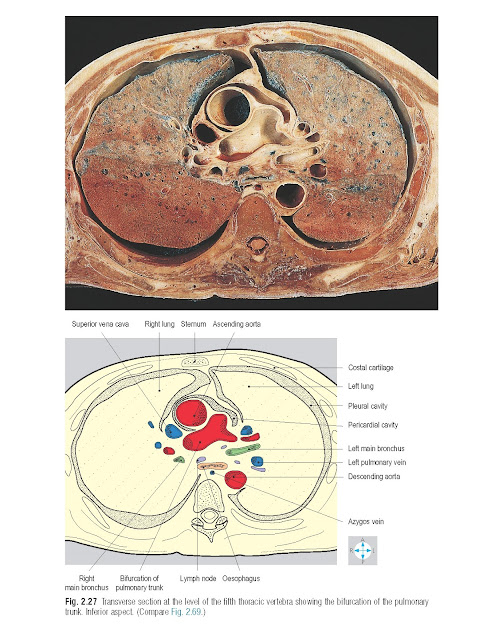
gives rise to the right and left main (principal) bronchi (Fig. 2.26).
The right main bronchus is wider and
more steeply inclined than the left (Fig. 2.27). As a
consequence, inhaled foreign bodies are more commonly found in the right main
bronchus. The main bronchi give rise to lobar (secondary) bronchi, which are
confined to their respective lobes. On the right, the upper lobe bronchus
arises outside the hilum in the lung root, whereas on the left, the lobar
bronchi arise entirely within the lung. In each lobe, further subdivision
occurs into segmental (tertiary) bronchi, which are constant in position and
supply specific portions of lung called bronchopulmonary segments. Each lobe
consists of a definite number of these segments. Within individual segments,
the bronchi further subdivide into bronchioles, then respiratory bronchioles,
which in turn lead into the alveolar ducts and alveoli. Bronchial arteries
derived from the descending thoracic aorta accompany and supply the major
bronchi. Venous return from the bronchi is through bronchial veins that
terminate in the azygos venous system (p. 63).
The right and left pulmonary arteries
divide into branches that correspond to and accompany the subdivisions of the
bronchi within the lungs. The bronchi and pulmonary arteries lie centrally in
the bronchopulmonary segments. The arteries ultimately give rise to pulmonary
capillaries in the alveolar walls. Oxygenated blood drains from these
capillaries into tributaries of the pulmonary veins that occupy intersegmental
positions. These vessels empty into two pulmonary veins, which usually emerge
separately through each hilum (Figs 2.24 & 2.25) and drain into the left
atrium.
Autonomic nerves
The pulmonary plexus, most of which
lies behind the lung root, contains both sympathetic and parasympathetic
fibres, which accompany the bronchi into the lung. Sympathetic nerves originate
in the upper thoracic ganglia of the sympathetic trunk and supply smooth muscle
in the walls of the bronchi and pulmonary blood vessels. The parasympathetic
fibres are derived from the vagus nerves and supply bronchial smooth muscle and
mucous glands.